Nvidia has made a groundbreaking move in the artificial intelligence industry by releasing its NVLM 1.0 family of open-source models.
Among these, the NVLM-D-72B model stands out with its ability to compete with proprietary systems from leading companies like OpenAI and Google.
Breaking with industry norms, Nvidia has decided to make the model weights of NVLM-D-72B publicly available and promises to release the training code, opening doors for researchers and developers worldwide.
This decision represents a significant shift away from the trend of keeping such advanced AI systems closed to the public.
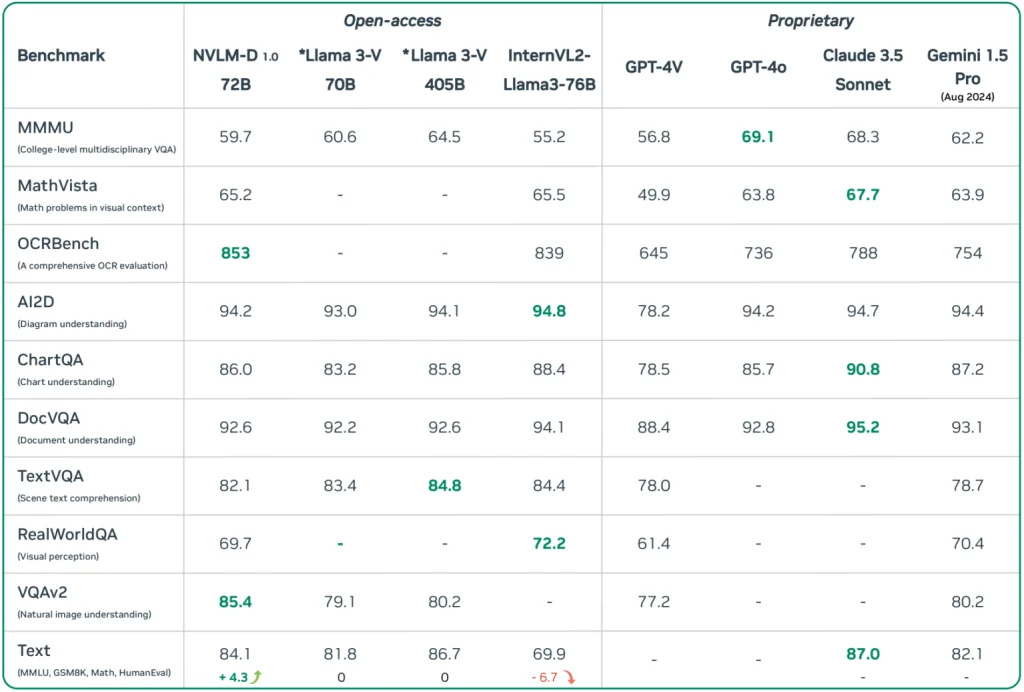
The NVLM-D-72B, carrying an impressive 72 billion parameters, showcases remarkable performance in both vision-language and text-only tasks.
This versatile model can process complex visual and textual inputs, interpreting memes, analyzing images, and solving mathematical problems with precision.
In a notable achievement, the model enhances its text-only task performance by an average of 4.3 points across various benchmarks following multimodal training, surpassing the usual decline observed in similar models.

The AI community has reacted enthusiastically to Nvidia’s initiative.
One highlight of this new model is its close competition with Meta’s LLaMA 3.1 in mathematical and coding evaluations, coupled with superior vision capabilities.
This accessibility could potentially accelerate AI research and empower smaller organizations and independent researchers to contribute meaningfully to the field.
The NVLM 1.0 project also introduces innovative hybrid architectures in multimodal processing, possibly paving new pathways for AI research.
However, this release also raises ethical concerns. Making such powerful AI technology available to a broader audience brings worries about misuse and the necessity for responsible AI practices.
Nvidia’s open-source strategy is seen as a direct challenge to established AI industry leaders, possibly prompting them to reconsider their approaches to proprietary systems.
This development may accelerate AI progress, urging other tech companies to follow suit.
Yet, as AI becomes more accessible, the ethical implications of its misuse become more pronounced.
The AI community now faces the challenge of fostering innovation while ensuring responsible use.
Nvidia’s revolutionary step may also influence the business models in the AI domain, as companies rethink their strategies to maintain a competitive edge.
The full implications of the NVLM 1.0 release will unfold in the coming months.
It might lead to unprecedented collaboration and innovation or highlight the ethical challenges of unrestricted access to powerful AI.
In either case, Nvidia has indisputably shaken the landscape of the AI industry, presenting a new chapter in open-source AI development.
